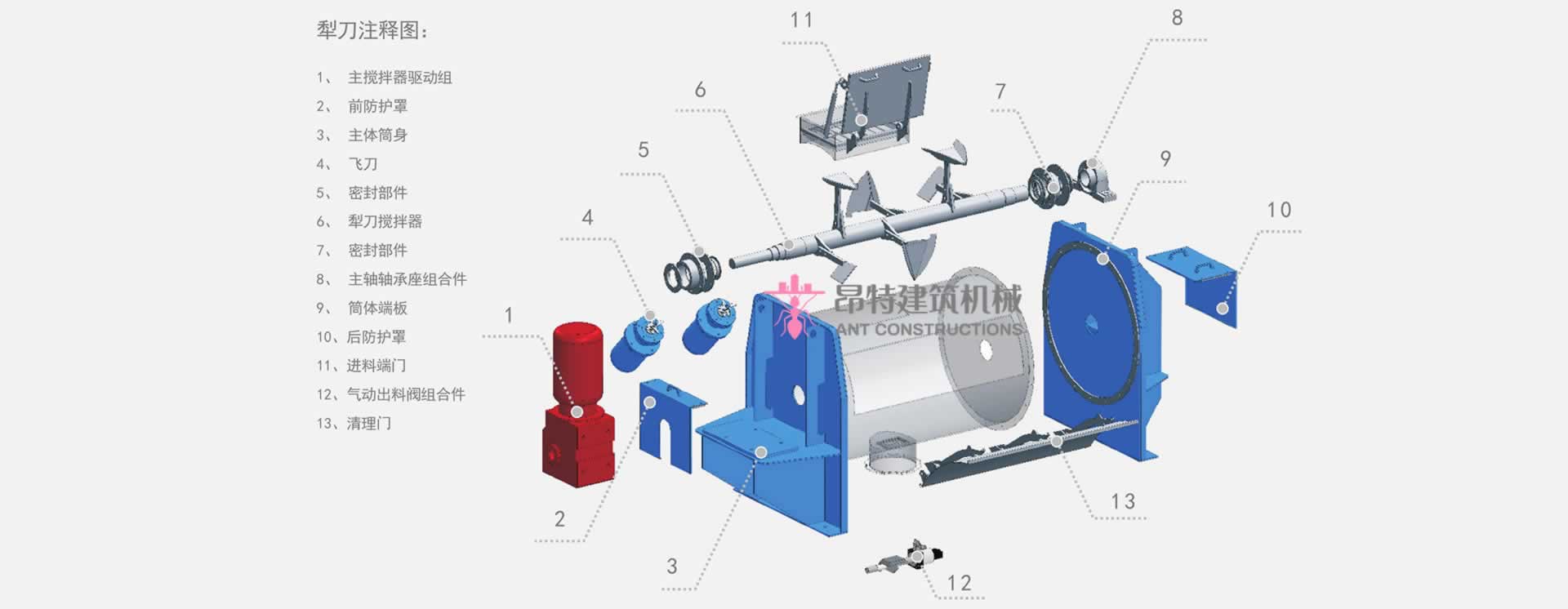
Motor errors and maintenance in tile adhesive manufacturing plant
Author:ANT CONSTRUCTIONS Comefrom: Createdate:2020/11/2 8:36:19 Hits:74
Motor errors and maintenance in tile adhesive manufacturing plant
Common erros in tile adhesive manufacturing
The motor shaft jump caused the bearing overheat
First, the shaft jump problem of the dry mortar mix making plant motor in tile adhesive manufacturing : In general, deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings are more commonly used. When installing, one end is positioned axially, and the other end is axially floating. Regarding the motor shaft jumping, firstly you should check how is the axial positioning done and to see the positioning if reliable. If reliable, for deep groove ball bearings, its axial jumping should be its axial clearance. Generally not too big. But it depends on the radial clearance. For cylindrical bearings, N and NU series can not be used as positioning bearings. If use them for positioning, the shaft jumping is certainly too much.
Second: People so called the bearing jumping lead to bearing burn. If the positioning bearing bears excessive axial load, it will cause the bearing to burn. Therefore, it necessary to confirm the max axial load when choosing a positioning bearing to make sure the bearing you selected can bear it. If it is a cylindrical stick bearing of the NJ series, this axial load is completely borne by the sliding part, so it not workable. For deep groove ball bearings, its axial capacity is at most a quarter of the radial, it is different for different bearings.
Check if used deep groove ball bearing in the motor
If a deep groove ball bearing is used, is it necessary to fix one end of the bearing to the shaft, and then fix the bearing on the end cover to limit shaft jumping? Now many shafts can move back and forth, it still jump by adding one corrugated gasket.
The dry mortar mix plant motor shaft system generally need axial positioning. So there will need to be one end as the positioning end and another end as the moving end.
The wave spring is not used for positioning, but for axial preload. Therefore, for cross-positioned motors,here must be axial movement caused by spring washers. If you want to control, you should make a traditional positioning end and a non-positioning end. Then add a spring washer to the non-determined end, and that will solve the problem.
The low-power brushed DC motor
In the low-power brushed DC motor, one end adopts a ball bearing, and the other end adopts a spherical oil-impregnated bearing. How do you choose a ball bearing and the tightness of the fit with the shaft and bearing chamber for this structure. (The shaft diameter is 8mm, the bearing thickness is 8mm, the opening of the two bearing gears is about 90mm, the motor noise requirements are very high). Generally speaking, j5\6 is used for the inner ring, and H7 is used for the outer ring, but this is not absolute. In addition, to control the motor noise, from the bearing speaking, you need to select a special clearance and grease (if the noise requirements are high). The clearance can be smaller, but can not too small, otherwise it will lock up. Choose a grease with a lower viscosity.
The bearing run on the outer ring
There are two situations for this problem: first, used an aluminum bearing chamber, sencond, used a general cast iron or other iron bearing chamber.
used an aluminum bearing chamber
1. For the first one situation, since the expansion coefficient of aluminum is twice of iron, the correct fit you use during installation, but will loosen after the temperature rises, jumping will be occur. There are two ways. First, step up cooperation during installation. I don't recommend this method. Although the problem can be solved, it is more annoying during installation. Second, use a rubber ring and open a groove in the bearing chamber. The groove depth is 0.8 times thickness and 1.4 times width of the rubber ring. Remember, the data I gave cannot be changed, otherwise, it will be has problems, I will elaborate on it if you are interested.
used a general cast iron or other iron bearing chamber.
2.Second, iron bearing room, I suggest you check the fit of the bearing room, this problem is much simpler than the above, mainly because of loose!
the degree of cooperation between the outer ring of the bearing and the bearing chamber
According to the information of some bearings (NSK, SKF): the degree of cooperation between the outer ring of the bearing and the bearing chamber is that the outer ring of the bearing can creep in the bearing chamber, so that the outer ring of the bearing will be uniformly worn and thus prolong the service life of the bearing , Is it reasonable? The peristalsis is axial peristalsis which is to absorb axial expansion. (It is definitely not circumferential creep. The circumferential direction is definitely not good. It destroys the rolling state of the bearing.) However, I personally do not agree with the statement that the outer ring is uniformly worn. The purpose of peristalsis is not to wear. After wear, the relative position and load of the bearing will change, which is not necessarily. If creep wear is good, there is no need to invent a bearing that can adjust axial elongation.
The bearing used in the vibration motor of the dry mortar mix plant mortor.
The vibration motor of the dry mortar mix plant is a very interesting topic. When selecting a bearing, it should be noted that the calculation of bearing load is already different, and the acceleration of vibration should be considered. The equivalent load obtained in this way is different, so the selected bearing size is different. Also pay attention to the choice of cage, in many cases use copper cage. (But not dogmatic, it depends on the situation) Also, some brands, such as SKF has special bearings for vibrating screens which are specially developed for vibration occasions. The cage is very strong.
In addition, when installing the bearings of the vibration motor used in dry mortar mix plan, pay attention to the choice of lubrication. Sometimes grease with EP additives is used. And the lubrication interval should be shortened, and the corresponding calculation should be carried out according to the instructions of different bearing manufacturers.
When assembling, we must pay attention to the tolerance fit that the designer chooses. The fit of the shaft and the bearing chamber in vibratin motor should be a tight fit. Please refer to the corresponding bearing manufacturer's data for specific data. But if you cooperate tightly, you must consider whether the remaining clearance is enough...
The fit between the shaft and the inner ring
What is the appropriate fit between the shaft and the inner ring of the bearing and the end cover and the outer ring of the low-power asynchronous motor? In addition, is the noise of the outer rotor fan motor starting up related to the bearing?
For small motors, the matching options should have these aspects: First, for aluminum shell motors, usually the thermal expansion coefficient of aluminum is larger than that of cast iron, so when you choose the matching, it is recommended to tighten it by one stop than that of cast iron. Second, for the motor of the cast iron frame, just use the cooperation in the manual. Third, if the aluminum injection rotor is matched in the manual, please add an o-ring on the outer ring to avoid running circles.
For outer rotor motors, if the bearing rotates on the outer ring, then use a tight fit for the outer ring and a transitional fit for the inner ring. The choice of coordination is the same as above, but in reverse.
What are the recommended applications of copper cage bearings and engineering plastic cage bearings (on the motor)?
What are the recommended applications of metal dust cover and plastic dust cover bearings?
The bearing cages of various motor brands used in dry mortar mix plant are divided into brass, steel, and engineering plastics according to different materials. These three have many applications in motors.
For engineering plastic cages, the performance of each manufacturer is slightly different, but generally similar. This kind of cage is light in weight and suitable for high-speed occasions. And the failure mode of this kind of cage is not a sudden burst, so it is more suitable for some occasions where sudden shutdown is not allowed. But for mining machinery, this kind of cage is not suitable for use due to safety considerations. (Mainly because it does not break all at once when it is broken, and the temperature rises a little bit, which is dangerous for explosive occasions.) At the same time, this kind of cage has a temperature limit, generally between minus 40 degrees and 120 degrees. Otherwise the cage material will be a problem.
For the brass cage, there is basically no obstacle, but it cannot be applied to the environment with ammonia.
For steel cages, there are no restrictions. But generally small bearings do not have the same cage, and large bearings do not have a steel cage.
For dustproof, the general iron cover is only dustproof and has no sealing effect. There is no temperature limit. At the same time, the speed performance is the same as that of an open bearing.
For rubber seals, the temperature of ordinary rubber seals has a range that cannot exceed 120 degrees, and high temperature fluorine rubber is 180 degrees. This has sealing performance, but the speed of the sealed bearing is lower than that of the open bearing.
In the mechanical design book,
I only see how to choose the tolerance of the shaft and hole. As for how to choose the clearance, it is relatively rare or vague. How to choose the original clearance, installation clearance and working clearance? I see in ordinary mechanical design books, normal load, 120mm journal, all choose m5 tolerance (+0.013, +0.028), average +0.0205; basic clearance group (+0.015, + 0.041), average +0.028; bearing bore (0, -0.02), average -0.01. In this way, the average interference becomes +0.0305 after installation, and the bearing clearance only averages +0.028, which becomes negative clearance during operation. Is this appropriate?
First of all, I want to talk about your previous question. There is no suggestion to choose the clearance in the manual. This is because the clearance of the bearing is determined at the time of production, so when you use it, you have to choose the appropriate tolerance fit with its clearance. And not the other way around, because of your tolerance and fit to customize the bearing. Because the bearings are standard parts. It can be seen from the above that, in fact, the essence of choosing the clearance is to choose a suitable tolerance fit. Under normal circumstances, the internal clearance when the bearing is working should be a very small positive value (except for tapered roller bearings and angular contact ball bearings). Therefore, the working clearance you mentioned has become a negative value, which is probably a bad choice. As for how big, different types of bearings have different ranges. For example, the recommended working clearance of small and medium-sized deep groove ball bearings is 4-11um under normal temperature and industrial and mining conditions. (Note the premise, not all bearings, nor large deep groove balls.)
Secondly, when you talked about the change of bearing clearance, you just talked about the change of tolerance effect. In fact, there is another aspect to pay attention to, that is, the change of clearance caused by thermal expansion and contraction. This must be taken into consideration when calculating.The method of selecting the clearance is to subtract the small clearance caused by the tolerance fit from the original clearance, and then subtract the amount of clearance change caused by the temperature change, and the working clearance obtained is in line with the basic operating conditions.
the following calculations have been made for your bearing:
Since you did not give the temperature distribution (shaft, bearing chamber), I only calculated the tolerance effect. Even so, since you did not give the tolerance of the bearing chamber, my calculation is only assuming the bearing chamber H7.
If it is the shaft diameter of n6, if the 6324/C3 bearing is selected, the remaining internal clearance is -0.005 to 0.049. If the fit is changed to m6, the remaining clearance is: 0.003 to 0.057. It can be seen from here that it is not actually you need to choose C4, but you need to review your own tolerance fit problem.
In addition, you said that you want to leave room for thermal expansion. I think this argument needs to be considered. Because, in fact, the so-called thermal expansion space, inside the bearing, has the greatest influence on the clearance. If you choose the right match and choose the right clearance, you will naturally have it. Don't leave it alone.
One last general recommendation: For industrial motors, general operating conditions. C3 clearance is recommended (except for small motors). Tolerance fit is selected in accordance with the manual, unless there is a special change in temperature load. (Trust the manual, the numbers in there are all calculated.) Even in my personal work, I only do clearance calculations when there are special requirements for temperature or operating conditions. In general, select directly according to the manual. (To be honest, I used to do calculations a lot in the past, but I found that in many cases, after a big circle, I still return to the manual data. So, at this point, I believe the manual. Of course, it is the same sentence, the special working condition manual Not applicable)
After the motor with high vibration in the putty powder mixer was disassembled, the grease in the bearing turned silver gray (originally milky white). What caused the problem? Is it normal for the bearing grease to change color, and what color the grease turns into is normal What degree of change is normal. Some bearing grease also changes color, from milky white to brown, and the discolored part is around the rolling element. What is the reason? If it becomes silver gray, it is due to tight fit and small clearance. It is caused by large friction, but the same bearing has the phenomenon of running circles on the outer ring. Why is this?
The grease may change color in the bearing, even if it is not placed in the bearing, it will change color. This is because:
First, there is an oxidation problem with grease. When the grease is left (or operated) for a period of time, it will have a lot of contact with oxygen. At the same time, the metal (the bearing itself) acts as a catalyst in this oxidation reaction. Therefore, when calculating the replenishment interval of grease in the bearing, the problem of oxidation should also be considered. Many greases now have antioxidant additives. This does not mean that there will be no oxidation.
Second, the bearing operation itself, the temperature (the bearing itself, or the environment) will change, which causes the base oil in the grease to continue to flow in and out of the thickener, and each time the base oil returns, it does not necessarily return completely. After such a long time, the performance of the grease will change and it will not be able to meet the lubrication, so it is necessary to re-apply lubrication. The color of grease with insufficient base oil may change. Also, if the temperature is abnormal, the performance of the grease will also change greatly, so that there will be discoloration. If the temperature is high, it will be carbonized. The color will become darker.
Third, impurities are mixed into the grease during the operation of the bearing. This kind of impurity may be peeled off by the bearing itself, or it may have entered from outside. It may be solid or liquid, and these will affect the properties of the grease.
In addition, you said that the fit is tight and the clearance is small, causing the grease to change color. This reasoning should be like this: the fit is tight, the working (remaining) clearance is small, the bearing load area is increased, and the heat is generated, which leads to the degeneration of the grease and the color change of the grease. As for the running laps, first, there may be a problem with the fit of your bearing chamber. Second, the internal clearance is too small and the friction is too large, which leads to running laps. The latter possibility cannot be achieved by adjusting the fit. The more you adjust, the worse.
Also, you are talking about judging whether the situation is normal based on the color of the grease. It is very difficult to judge this point. Different lubricating greases have different internal additives, different operating conditions, and different temperature ranges. It is impossible to have a unified standard. Even the same type of grease may have slightly different formulas due to different batches on the market. Please do not use this color change as a basis, it is not reliable.
The inner ring of the motor bearing of the putty powder mixer is fixed and the outer ring rotates.
You are talking about a fixed inner ring and a rotating outer ring. This is just the opposite of general bearing operating conditions. There are several suggestions:
First, tolerance fit: In general bearings, the inner ring rotates and the fit is tighter than the outer ring. The outer ring is looser. The reason is that the outer ring mainly plays a supporting role and does not have a large rotating force. (Microscopically, the outer ring will creep relatively, but not much) What you said is just the opposite, that is, the forces on the two bearing rings are just opposite. Therefore, the tolerance fit must be reversed. The actively rotating ring fit will be relatively tight.
Second, the choice of clearance: basically the choice of clearance is related to temperature and tolerance. If you just reverse the tightness of your outer ring tolerance, then the impact before and after the change is not particularly large (but certainly, it cannot be ignored in precision occasions). Generally speaking, it can be considered that it is caused by tolerance matching with ordinary bearings. The same changes. As for the temperature, it has nothing to do with which circle rotates, it mainly depends on your external heat source. So there is not much change. In short, the clearance can basically be selected according to the past.
Third, the putty powder mixer motor is lubricated. Please note that if it is a sealed bearing, please do not use the dust cover, it will definitely leak oil. Choose rubber seal. If it is a general open bearing, please note that the relubrication interval should be adjusted to half of the past.
A three-phase asynchronous motor, the bearing is selected φ45×φ58×7, it is easy to deform during installation? Because of the strict requirements on speed and noise, the axial clearance is small, the speed is low, and the noise is suitable; the axial clearance is large, and the speed is suitable , The noise is loud, what's the trick? There is a motor, the bearing is stuck, and after disassembly, a lot of black lumps are found in the bearing. What is it?
If you take a general industrial motor, this 618 series bearing is not very commonly used. This is a thin series bearing. You are right to be easy to deform.
This deformation comes from the influence of external deformation. It has something to do with your outside material. If it is made of aluminum, the impact is even greater. In addition, what part of the axial clearance you said is worth? Is the internal clearance of the bearing? For deep groove ball bearings, we mostly talk about radial, unless your application has special requirements and needs to be converted. Properly small clearance will indeed improve noise and vibration. But this does not mean good. When you make a factory test, the internal clearance may not be the same as the actual internal clearance. Because of temperature changes. Therefore, you may leave the factory well (if the operating temperature does not reach the actual working condition), but it will not work when it is actually running. If the gap is too small, it will naturally get stuck. Therefore, when choosing the clearance, it is necessary to choose the working clearance, so that when running, it should run to the same temperature as the working condition, and then look at the noise and vibration. This is correct.
In addition, if there are photos of the black things you mentioned, it would be great. It is stuck, the temperature must be high, maybe the bearing is peeling off? Could it be denatured grease? It may be pollution from the outside world. . ? There are many possibilities. Based on your description, I forgive my brother’s incompetence and cannot make a clear judgment.
There is a question that has been tied up for a long time. Ask the host about the loss of the motor bearing of the putty powder mixer? The selected bearing model is 6020zz (medium hole 15, outer diameter 35) production line off-line motor, when running at high speed, the no-load power is up to 200W, but if the motor runs continuously for 30 minutes, the power is only 50W. After waiting for the motor to completely cool down, the no-load power quickly dropped to 50W after starting the motor. After analysis, the problem appeared on the bearing. My understanding is: 1. The new bearing is caused by uneven grease distribution, 2. The viscosity of the grease has a certain relationship. If the grease with a relatively low viscosity is selected, it will affect the life. 3. The size of the bearing clearance, but the bearing after running-in will not have this problem. The noise requirements of the motor are very strict. There is no good solution for the time being. Please give me some advice! ! Thanks a lot
It is caused by the uneven distribution of grease inside the new bearing. You are right. At the beginning, the distribution of grease inside the bearing is uneven, and there is indeed a phenomenon of even grease in the early stage of operation.
The viscosity of grease has a certain relationship. If you choose grease with relatively low viscosity, it will have an impact on life. In fact, the key is that the well-known viscosity is also related to temperature. The higher the temperature, the lower the viscosity of the grease. . This will bring less loss. So what you said in the first half is correct, and in the second half, it should be said that the grease viscosity in time is suitable for bearing operation, not the bigger the better. There is usually a certain range, called the Kappa coefficient. When this number is between 1 and 4, high-quality viscosity is appropriate. If the high-quality viscosity is too large, it will cause temperature rise problems. Your problem is that at the beginning, all the temperatures are low, and the viscosity of the grease is high, so the loss is large. After a period of operation, the temperature rises, the grease becomes soft and the viscosity decreases, and the loss is small. Therefore, when choosing lubrication, it should be based on the operating temperature, and when the loss is made, it should also be based on a temperature. To eliminate the influence of temperature.
The size of the bearing clearance, but the bearing after running-in will not have this problem. The noise requirements of the motor are very strict. The bearing clearance has no direct effect on friction, but it has an effect on the number of rolling elements in the load zone, which indirectly affects the loss, but it is not important. It is not recommended to assess the loss by adjusting the clearance. You might as well put your energy elsewhere. However, for noise, the impact of the clearance is greater. The question I answered earlier mentioned specifically, you can check it yourself, I won't go into details.
Also, the problem you mentioned that bothers you, is it loss or noise? If it is a loss, then it is reasonable to say that a given bearing has basically the same loss, and it is difficult for you to change too much (based on the premise of normal use). At the same time, this has an impact on the total loss of the motor, about 0.6%. Let's spend more energy on electromagnetics
For noise, there is much to say. Due to space limitations, we cannot say all of them. General advice to you, deep groove ball bearing, choose C3 clearance, cylindrical roller bearing ordinary clearance. This is suitable for general industrial motors, except for special designs.
Do bearings of motors, generators and automobile generators have to use C3 clearance? Does the bearing use more common clearance or C3 clearance? What are the differences and advantages and disadvantages of 2Z, 2RZ, and 2RS? 4. I have a generator bearing, long-term continuous work at 70-90 degrees, 1500-3000 rpm, choose 6203/C3, shaft tolerance 17j5, aluminum housing, H7 or H6?
The first question: The category you mentioned includes all motors (motors and generators), so you are sure that your answer is uncertain.
The second question: This is related to the type of bearing, the type of motor, the load of the motor, the temperature, and other application conditions. It cannot be summed up.
The third question is that these three sealing methods are different. 2Z is a dust cover, not a seal, but has a rough ability to protect against solid pollution particles, so the English is shielder, not a seal. For the latter two (from what you said, it is very likely that you are talking about SKF bearings), one is light contact seal and the other is contact seal. Good contact seal protection ability. However, due to the contact of the seal, the speed capability of the bearing is the worst. (God is fair, if you give you the sealing ability, you won't give you the speed ability.) These three protection methods are the same. The better the sealing performance, the lower the speed ability.
The fourth problem is that the tolerance fit of the aluminum motor is one level tighter than that of the cast iron base. But this is not a good way. A good way is to add an o-ring to prevent the outer ring from running around.
Maintenance method of dry mortar mix plant motor
Dry mortar plant motor professional maintenance and repair process: cleaning the stator and rotor-replacing the carbon brush or other parts-vacuum F-level pressure dipping paint-drying-calibrate balancing.
The operating environment should always be kept dry, the surface of the motor should be kept clean, and the air inlet should not be obstructed by dust, fibers, etc.
When the thermal protection of the motor continues to operate, it should be ascertained whether the fault comes from the motor or the overload or the setting value of the protection device is too low. After the fault is eliminated, it can be put into operation.
The motor should be well lubricated during operation. The general motor runs for about 5000 hours, that is, the grease should be added or replaced. When the bearing is overheated or the lubrication is deteriorated during operation, the hydraulic pressure should be replaced in time. When replacing the grease, remove the old lubricating oil, clean the oil grooves of the bearing and bearing cap with gasoline, and then fill 1/2 of the cavity between the inner and outer rings of the bearing with ZL-3 lithium-based grease (for 2 poles) And 2/3 (for 4, 6, and 8 poles).
When the life of the bearing is over, the vibration and noise of the motor will increase significantly. Check that the radial clearance of the bearing reaches the following value, and the bearing should be replaced.
When disassembling the motor, the rotor can be taken out from the shaft extension end or the non-extended end. If it is not necessary to remove the fan, it is more convenient to take out the rotor from the non-shaft extension end. When pulling out the rotor from the stator, prevent damage to the stator winding or insulation.
When replacing the winding, you must write down the form, size, number of turns, wire gauge, etc. of the original winding. When you lose these data, you should ask the manufacturer to change the original design winding at will, which often results in one or several performances of the motor. Deteriorating, even unusable.